APY, or Annual Percentage Yield, is a measure used in banking to represent the yearly interest earned on an investment or savings account, including compound interest. It reflects the total return you can expect from your money over a year, taking into account both interest and the effect of compounding.
It is your key to understanding just that. It’s like a magic formula that tells you how much your money can flourish in a savings account or investment, taking into account both the interest rate and how often it compounds. Simply put, the higher the APY, the faster your money grows. So, if you’re aiming to make the most of your savings, keep an eye on that APY
What Is the Annual Percentage Yield (APY)
The Annual Percentage Yield (APY) is a measure of the total amount of interest earned on an investment over one year. Unlike the simple interest rate, APY takes into account compound interest, providing a more accurate picture of the investment’s growth potential. It’s a crucial factor to consider when comparing different savings accounts or investment options.
When you see a high APY, it means your money has the potential to grow faster over time. This is because the interest earned on your initial investment is reinvested, earning even more interest in subsequent periods. Essentially, APY helps you gauge the true earning power of your money and make informed decisions about where to save or invest.
Formula and Calculation of Annual Percentage Yield (APY)
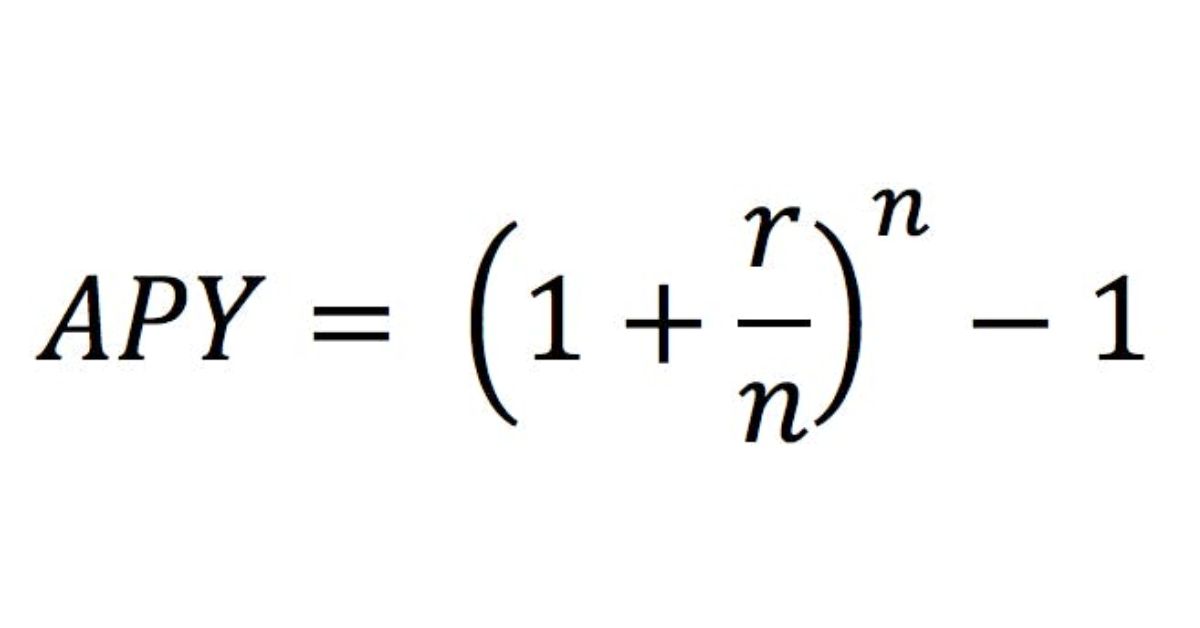
The formula for calculating Annual Percentage Yield (APY) involves the interest rate and the frequency of compounding. It’s expressed as: APY = (1 + r/n)^n – 1, where ‘r’ is the nominal interest rate and ‘n’ is the number of compounding periods per year. This formula considers how often interest is added to the principal amount, providing a more accurate measure of investment growth.
To calculate APY, simply plug in the interest rate and the compounding frequency into the formula. For instance, if a savings account offers a 5% interest rate compounded quarterly, you’d use 5% as ‘r’ and 4 as ‘n’ (since there are four quarters in a year). After plugging these values into the formula, you’ll get the APY, giving you a clearer understanding of the account’s potential earnings.
What APY Can Tell You
APY, or Annual Percentage Yield, offers a clear snapshot of how quickly your investment can grow over time. It factors in both the interest rate and the frequency of compounding, giving you a comprehensive view of your potential earnings. APY serves as a valuable tool for comparing different savings or investment options, helping you make informed decisions to maximize your returns.
Comparing the APY on Two Investments
When comparing the APY of two investments, higher APY indicates faster growth potential for your money. For instance, if Investment A offers a 3% APY while Investment B offers a 5% APY, choosing Investment B could yield greater returns over time. By considering the APY of each option, you can make a more informed decision to optimize your investment strategy and maximize your earnings.
APY vs. APR
| Aspect | APY (Annual Percentage Yield) | APR (Annual Percentage Rate) |
| Definition | Reflects the total return on an investment, including compound interest. | Represents the yearly interest rate on a loan or credit card, excluding compounding. |
| Calculation | Takes into account compound interest, providing a more accurate measure of investment growth. | Calculates the simple interest rate, disregarding compounding effects. |
| Importance | Crucial for evaluating investment growth potential and comparing savings or investment options. | Essential for understanding the cost of borrowing money and comparing loan or credit card offers. |
| Example | A savings account with a 5% APY means your money could grow by 5% annually with compound interest. | A loan with a 4% APR means you’ll pay 4% interest on the principal amount borrowed each year. |
| Key Consideration | Higher APY signifies faster growth potential for investments. | Lower APR indicates less expensive borrowing for loans or credit cards. |
Top of Form
Example of APY
- A savings account offering a 3% APY means that for every $1000 deposited, you could earn $30 in interest over one year.
- APY is crucial for evaluating the potential growth of investments like certificates of deposit (CDs) or high-yield savings accounts.
- Comparing APYs helps individuals choose the most lucrative savings or investment options for their financial goals.
- Investment vehicles with higher APYs typically offer greater returns over time due to the power of compounding interest.
- Understanding APY allows savers to make informed decisions about where to allocate their funds for optimal growth.
Variable APY vs. Fixed APY
| Aspect | Variable APY | Fixed APY |
| Nature | Fluctuates based on market conditions, economic factors, or changes in the underlying investment. | Remains constant for a specified period, regardless of market fluctuations or changes in interest rates. |
| Flexibility | Offers potential for higher returns if market conditions improve but carries the risk of lower returns if conditions worsen. | Provides stability and predictability, ensuring consistent earnings over the fixed period. |
| Risk | Carries a higher level of risk due to potential fluctuations in interest rates, which can impact investment returns. | Offers lower risk as the interest rate remains unchanged throughout the fixed period, shielding investors from market volatility. |
| Suitability | Suitable for investors seeking potential for higher returns and willing to tolerate market volatility. | Ideal for investors seeking stability and predictability in their earnings without exposure to interest rate fluctuations. |
| Examples | High-yield savings accounts with rates tied to prevailing market conditions. | Certificates of deposit (CDs) with fixed interest rates for a specified term, such as one year or five years. |
How Is APY Calculated?
APY, or Annual Percentage Yield, is calculated using a formula that takes into account both the interest rate and the frequency of compounding. The formula for APY is: APY = (1 + r/n)^n – 1, where ‘r’ represents the nominal interest rate and ‘n’ stands for the number of compounding periods per year. This calculation accounts for the effect of compounding, providing a more accurate measure of investment growth over time.
To calculate APY, simply plug the interest rate and the compounding frequency into the formula. For example, if a savings account offers a 4% interest rate compounded quarterly, you’d use 4% as ‘r’ and 4 as ‘n’. After inputting these values into the formula, you’ll arrive at the APY, revealing the potential earnings on your investment over the course of a year.
Related post: What Does Ach Stand For In Banking?
How Can APY Assist an Investor?
APY assists investors by offering a clear picture of how their investments can grow over time, considering compound interest. It enables them to compare different savings or investment options effectively, aiding in making informed decisions. By understanding APY, investors can optimize their investment strategies to maximize returns and work towards their financial goals efficiently.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is APY in banking?
APY stands for Annual Percentage Yield, representing the total interest earned on an investment over one year, accounting for compound interest.
How is APY different from APR?
APY reflects the earnings potential of investments, while APR indicates the cost of borrowing money, such as loans or credit cards.
Why is APY important for investors?
APY helps investors gauge the growth potential of their investments accurately and compare different savings or investment options effectively.
How is APY calculated?
APY is calculated using the formula: APY = (1 + r/n)^n – 1, where ‘r’ is the nominal interest rate and ‘n’ is the number of compounding periods per year.
What factors affect APY?
APY is influenced by the interest rate offered by the investment and the frequency of compounding, with higher rates and more frequent compounding resulting in higher APYs.
Related Post: What Is Plaid Banking?
Final Words
APY, or Annual Percentage Yield, is a crucial concept in banking that measures the total return on an investment over one year, accounting for compound interest. It provides investors with a clear understanding of how their money can grow over time, considering both the interest rate and the frequency of compounding.
Unlike simple interest rates, which only consider interest on the principal amount, APY takes into account the effect of compounding, where interest is earned on both the initial investment and any previously earned interest. This makes APY a more accurate measure of investment growth and allows investors to compare different savings or investment options effectively to maximize their returns.












